 netty记录
netty记录
#Netty
# NIO概念
non-blocking io非阻塞IO
# Channel & Buffer
Channel 类似与Stream 用来读写数据的双向通道
Channel 将数据读入 Buffer ,Buffer也可以写入Channel,
Stream 要么输入 要么输出 不会缓冲数据
# 常见channel
FileChannel 文件
DatagramChannel UDP
SocketChannel TCP
ServiceSocketChannel TCP 服务器端
# Buffer 缓冲取
- ByteBuffer 抽象
- MapperByteBuffer
- DirectByteBuffer
- 堆内存
- 读写效率低
- 受GC影响
- HeapByteBuffer
- 直接内存,少一次拷贝
- 读写效率高
- 不受GC影响
- 需要调用系统函数,分配效率较低 使用不当会内存泄漏
- ShorBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- CharBuffer
# Selector
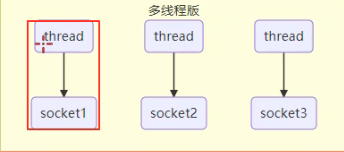
# 多线程版本
一个线程对应一个Socket
- 内存占用高
- 每个客户端占用一个线程
- 线程切换上下文成本高
- cpu核心数不足,多出线程需要进行切换
- 只适合连接量少场景
# 线程池版

- 阻塞模式下,一个线程只能处理一个Socket连接
- 在Socket处理区间,线程会一直占用,不能做其他事情
- 适合短连接场景
# Selector 版本
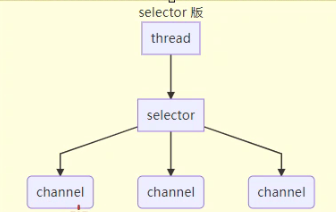
- 用一个线程管理多个Channel,
- selector 的select()会阻塞监听取Channel上的读写事件,返回给线程去执行 但是Channel本身是非阻塞模式的,不会让线程固定在Channel上
- 适合连接数多,流量低场景
# ByteBuffer
# JAVA类
public abstract class ByteBuffer
extends Buffer
implements Comparable<ByteBuffer> {
//开始指针
private int position = 0;
//写入限制
private int limit;
//容量
private int capacity;
/**
* 切换读模式
* limit == position写入数据后的下标 ,也就是数据长度
* position 归零 每次读取数据增加下标
* @return Buffer
*/
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
return this;
}
/**
* 切换写模式
* position 归零,每次写入增加下标
* limit == capacity == 数据最大容量
* @return Buffer
*/
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
return this;
}
}
# 图解
# 初始化
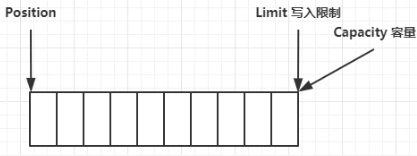
# 写模式 clear
- position 归零,每次写入增加下标
- limit == capacity == 数据最大容量
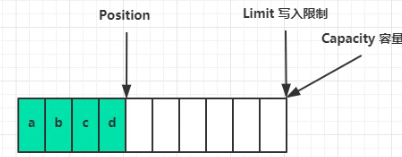
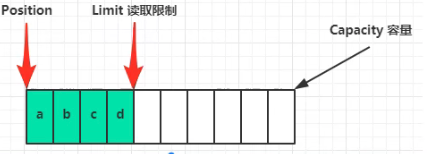
# 读模式 flip
- limit == position写入数据后的下标 ,也就是数据长度
- position 归零 每次读取数据增加下标
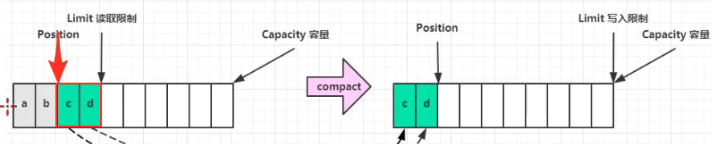
# compact 未读取数据压缩,切换写模式
- position ==剩余数据长读
- limit == capacity == 数据最大容量
# API
# 分配空间
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
# 写入数据
channel.read(buffer);
或者
buffer.put((byte) 1);
# 读取数据
channel.write(buffer)
或者
//buffer.get() 会移动 position 指针
buffer.get();
# 重复读取
//position 指针归零
buffer.rewind();
//重新读取
buffer.get();
或者
//get(i) 不会移动指针
buffer.get(i);
# mark & reset
mark 将当前 position 标记,reset将 position 重置到 mark
# 转换
参考 TestByteBufferConvert
# 黏包/半包
参考 TestExamBufferStickyPackage
# FileChannel
- FileChannel 只能工作在阻塞模式下
- 不能直接获取FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream,FileOutputStream,RandomAccessFile 的 getChannel获取
- FileInputStream 得到的 channel 只能读
- FileOutputStream 得到的 channel 只能写
- RandomAccessFile 得到的 channel 根据构造时的读写模式决定
- 处于性能考虑 channel 会将数据缓存而不是直接写入磁盘,通过force(true)可立即写入磁盘
#网络编程
# 阻塞模式
# 非阻塞模式
##selector多路复用 单线程配合Selector 实现多路复用,仅针对网络IO
# 消息边界
问题原因
客户端ByteBuffer容量过小,客户端消息过大,消息将会被多次读取造成截断
类似与拆包黏包概念
解决方案
- 与客户端约定固定长度
- 弊端,照成空间浪费
- 定义分隔符,自行黏包
- 效率低
- TLV格式 ,即Type(类型),Length(长度),Val(内容)
- 根据类型和消息长度,分配ByteBuffer
- HTTP 1.1 TLV
- HTTP 1.2 LTV
# 总结
select 何时不阻塞
- 事件发生时
- 客户端发起连接时 触发 accept事件
- 客户端发送数据时,正常,异常关闭 触发read事件,数据大于缓存区 会多次读写
- channel 可写时
- linux 发送nio bug时
- select.wakeup(),select.close(),
- 所在线程 interrupt
Netty
#EventLoop

#Channel

#为什么要异步
- 单线程没法异步提高效率,必须配合多线程和多核CPU
- 对系统而言异步没有缩短响应,反而有所增加 (线程切换相比单线程需要耗时),多出来的时间,提高了系统的吞吐量 (单位时间内处理请求的数量)
- 使用异步的前提是,要合理的对任务进行拆分
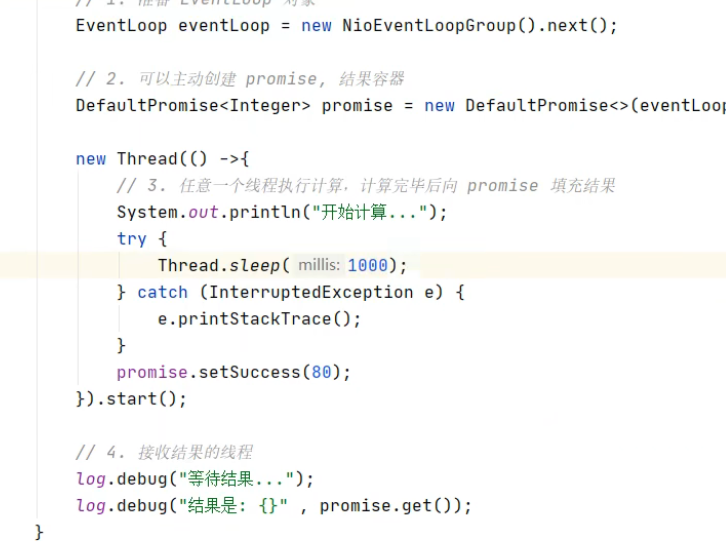
# Future & Promise

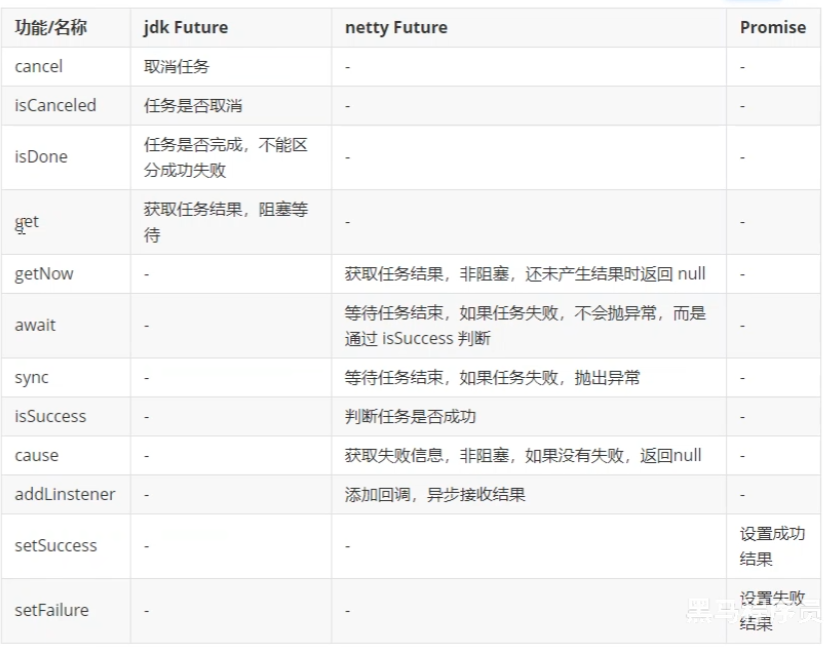
# Future 使用

# Promise 使用
# ByteBuf
# 直接内存 & 堆内存
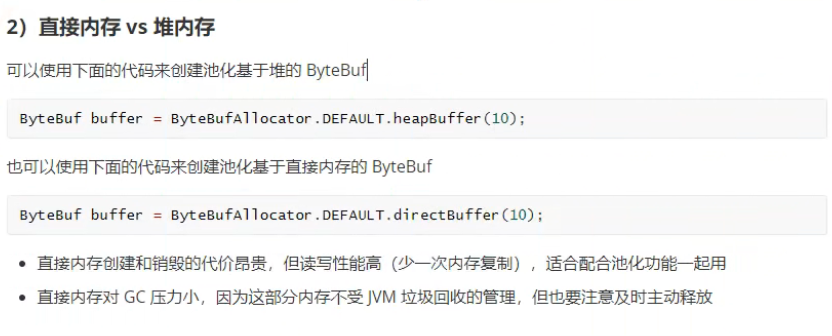
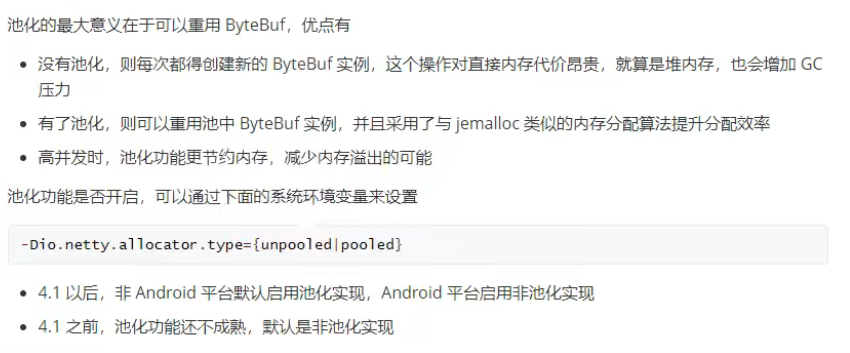
# 池化
# 写入扩容

#
# 黏包 & 半包
# 发生原因
- 滑动窗口
- 当发生方 发送的数据大于接受方缓存区的时候,出现半包
- 当发生方 发送的数据小于接受方缓存区的时候,出现黏包
# 解决办法
# 短链接
发送方发送一次数据后直接断开
能解决黏包问题,没法解决半包问题
# 定长解码器
双方定义发送数据长度,客户端发送消息后补全长度
例如:
约定长度10
客户端
发送: 12345 ,ABCDEFG
实际发送: 12345_____ABCDEFG___
服务端
第1次接受:12345_____
第2次接受:ABCDEFG___
参考:
netty 提供 FixedLengthFrameDecoder
# 行解码器
new LineBasedFrameDecoder(100);
new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(100, ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer())
# LTC解码器
//长度偏移量
int lengthFieldOffset = 0;
//长度属性 占用长度
int lengthFieldLength = 4;
//调整长度,再之后为内容长度
int lengthAdjustment = 6;
//需要剥离的字节
int initialBytesToStrip = 10;
//最大帧
int maxFrameLength = 1024;
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(maxFrameLength,
lengthFieldOffset,
lengthFieldLength,
lengthAdjustment,
initialBytesToStrip
)
# Http协议
//自定义http协议 》》》》》》
//HttpServerCodec http 编解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//自定义http协议 《《《《《《
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>(){
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext chx, HttpRequest httpRequest) throws Exception {
log.info("HttpRequest {}",httpRequest.decoderResult());
log.info("HttpRequest {}",httpRequest.method());
log.info("HttpRequest {}",httpRequest.uri());
log.info("HttpRequest {}",httpRequest.protocolVersion());
DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(httpRequest.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
String respContentStr = "<h1>welcome to my server</h1>";
byte[] bytes = respContentStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
response.headers().setInt(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH,bytes.length);
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
chx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpContent>(){
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, HttpContent httpContent) throws Exception {
log.info("HttpContent {}",httpContent.content().toString());
log.info("HttpContent {}",httpContent.retain().toString());
log.info("HttpContent {}",httpContent.retainedDuplicate().toString());
log.info("HttpContent {}",httpContent.touch().toString());
log.info("HttpContent {}",httpContent.decoderResult().toString());
}
});
# 自定义协议
自定义协议 要素
- 魔数 -判断是否有效数据包
- 版本号, 可以支持协议升级
- 序列化算法
- 指令类型 登录 注册等业务
- 请求序号,为了双共通信,提供异步功能,按序号对于请求和响应
- 正文长度
- 消息正文
如何构建
/**
* 必须配合 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用
* 确保消息完整
*
* MessageToMessageCodec 支持分享
* ByteToMessageCodec 不支持分享
*/
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf,Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message message, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
//1 写入 4 字节 魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte [] {1,2,3,4});
//2 写入 1 字节 版本
out.writeBytes(new byte [] {1});
//3 写入 1 字节 序列化方式 : 0 jdk 1 json
byte serialization = 1;
out.writeBytes(new byte [] {serialization});
//4 写入 1 字节 指令
out.writeByte(message.getMessageType());
//5 写入 4 字节 序号
message.setSequenceId(256);
out.writeInt(message.getSequenceId());
//6 为了保持协议 为2的n次方 使用1个无意义的字节填充
out.writeByte(0xff);
if(1 == serialization){
log.info("出站 编写协议 java 序列化 ");
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(message);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
//7 写入 4 字节 长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
//8 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
}else {
log.info("出站 编写协议 json 序列化 ");
}
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
//得到 魔术
int magicNumber = in.readInt();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:魔术 {}",magicNumber);
//得到 版本
int version = in.readByte();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:版本 {}",version);
//得到 序列化方式
int serialization = in.readByte();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:序列化方式 {}",serialization);
//得到 消息类型
int messageType = in.readByte();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:消息类型 {}",(256+messageType)%256);
//得到 序号
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:序号 {}",sequenceId);
//得到 一个无效字符
in.readByte();
//得到 长度
int length = in.readInt();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求:长度 {}",length);
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
if(1 == serialization){
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Message message = (Message)ois.readObject();
log.info("入站解析协议 此次请求 消息:{}",message);
out.add(message);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024,12,4,0,0),
new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG),
new MessageCodecSharable(),
new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("接受到入站消息:{}",msg);
}
}
);
//出站 encode 编写协议
LoginMessage loginMessage = new LoginMessage("曹诗韵","123456");
channel.writeOutbound( loginMessage);
//入站 decode 解析解析
ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
new MessageCodecSharable().encode(null,loginMessage,new ArrayList<>());
channel.writeInbound(buffer);
}
}
上次更新: 2026/02/27, 03:03:58
